The 2023 Buyer’s Guide to Furnaces
If you’re not prepared, replacing your aged or malfunctioning heating system can be overwhelming. Checking online reviews, asking family, friends and neighbors is a great way to discover the best Raleigh furnace installers. We hope to provide the best information in this furnace buying guide to better help you choose the right furnace for your home.
In This Raleigh Furnace Buyers Guide You'll Learn:
Looking for Furnace Tips?
In the following section, we discuss the common subjects and terms you will encounter while researching and purchasing a furnace. We also discuss when to replace your furnace or HVAC unit, what size furnace you need, and furnace efficiency ratings.
How a Furnace Works
- A thermostat activates the furnace, turning it on
- A gas control valve opens and regulates the fuel pressure to the burners.
- The pilot flame or ignitor ignites the fuel and fires directly into the primary heat exchanger.
- The hot exhaust gases move through the internal heat exchanger passages to heat the metal
- The exhaust gases then exit through a vent pipe to the outdoors.
- A blower assembly then moves air over the hot external surface of the heat exchanger.
- This hot air is then circulated through the duct system within the home to heat each room.
- Finally, once the thermostat registers heat levels that match the set temperature, the furnace shuts off.
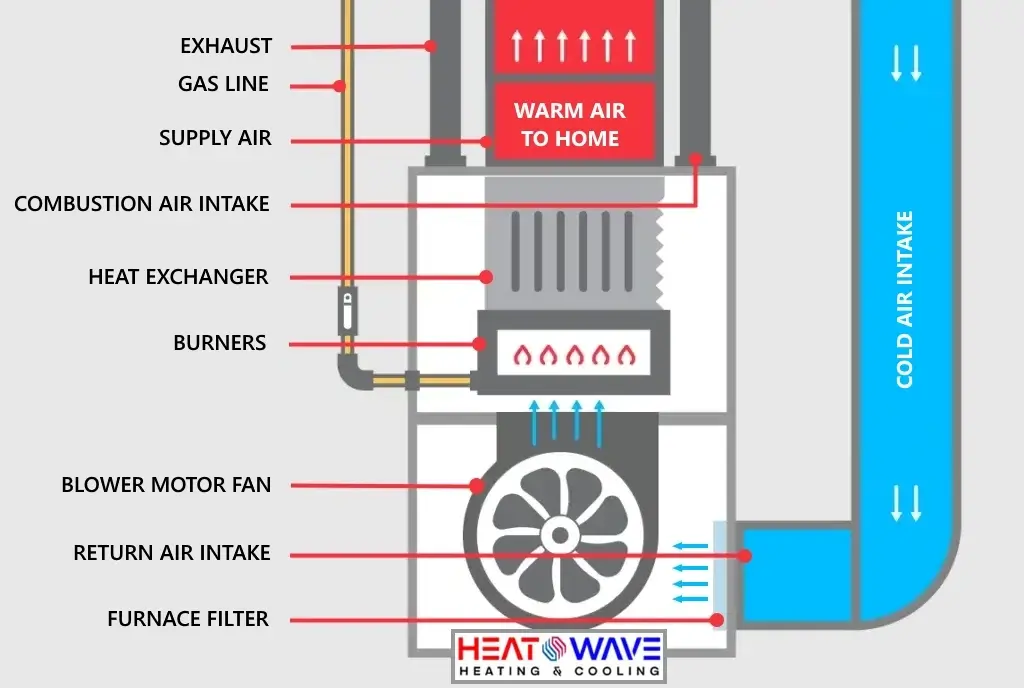
Most furnaces contain the following parts:
- Thermostat – controls on/off operation of the furnace
- Draft hood or fan
- Burners
- Pilot light or igniters
- Gas control valve
- Circuit board(s)
- Heat exchanger
- Blower assembly
When to Replace Your Furnace
Replacing a furnace can be a complex process, and we suggest consulting an HVAC expert about the decision. Here are a few guidelines you can use to determine if it’s time to have a consultation:
- Your furnace is 15+ years old
- Your furnace needs frequent repairs
- There is an extreme increase in energy bills, even when your thermostat is set on low
- The furnace is making loud, scraping, banging or other unusual noises
- Inconsistent temperatures during operation
What Determines Furnace Efficiency
AFUE Rating
Furnace efficiency is measured by its AFUE rating. This shows how much fuel is converted into heat versus how much energy is lost during the combustion process.
Natural gas furnaces sold in Wake County, NC must be high-efficiency with an AFUE rating of 90% or more. The most efficient units have a rating of 98-99%. Furnaces installed by AskHVACPro run by 95-96.5% efficiency with a few models as high as 98% and 99%.
As you determine your desired efficiency, keep in mind that AFUE may decline over the years because of dirty components, aging of the appliance and its parts, damaged parts, dirty furnace filters or if regular furnace maintenance isn’t performed.
In order to get the most life out of your furnace, annual furnace maintenance should be performed by a licensed North Carolina furnace or HVAC technician.
Furnace Model Tier and Fan Speeds
Aside from the AFUE rating, you should also consider the furnace model and the different stages of operation for the fan motor. There are three types of fan speed tiers – single stage, multi-stage, and variable stage. While there are three types of motors installed in furnaces, government regulations dictate that all new furnaces sold in the United States must include a multi-stage or variable stage fan motor.
Single Stage
Multi-Stage
Variable Stage
Variable stage furnaces and blowers operate at peak efficiency which allows for the furnace heating and fan speed to meet the needs of the home.
Finding the Right Furnace to Meet Your Heating Needs
There are almost a dozen variables that determine the ideal furnace for your home. Some of the factors include:
- The size, layout and age of your home
- The duct system’s air flow capacity
- How many windows in your home
- How well insulated your home is
- How well the older furnace was maintained
- What air conditioning system you have and it’s age
We encourage you to consult with an AskHVACPro to make sure your home’s specific needs are met.
Here are a few of the topics an HVAC expert should be ready to discuss with you.
Furnace Energy Source
Furnace Size
- Design Load: cis calculated to help determine the right furnace size by measuring the layout, orientation, insulation, and overall design of the home.
- Extreme Load: is calculated to help ensure that the furnace can provide more heat than what is lost during extreme temperatures. This measurement can help determine whether more insulation is needed to prevent air leaks or whether to consider a larger capacity furnace.
- Part Load: is calculated to determine how your furnace performs during average temperatures.
Other factors include:
- How many people living in the home
- Ceiling height
- Windows
- Doors
- Landscaping
- Flooring
- Number of appliances
How Much Does a New Furnace Cost?
The average cost for a new natural gas or propane high-efficiency furnace is $5,000 to $7,000. This price includes standard installation, at least a one-year warranty and all required licenses for installation. While it’s possible for a provider to install a furnace at a lower cost, there’s a higher likelihood that compromises were made with the components, workmanship, warranty coverage and post-installation support. There’s also a chance that the provider does not have the necessary insurance or licensing and certification.
Many factors can determine where the right furnace for your home falls in this price range, including homeowner preferences. Two people can own identical homes, but if one chooses a standard furnace and the other chooses one with the least environmental impact, better air circulation, latest technology, or advanced settings, those two furnaces will significantly vary in cost.
For a general view, here are the factors that have an impact on the cost of a new furnace:
- Furnace type: gas, oil, electric, or propane
- Environmental choices: energy efficiency, filtration options (presence of a chimney), and comfort-enhancing options
- Personal preferences: extended warranties, maintenance plans, and service guarantees
- Technical requirement: the size of your home, existing ductwork, type of heat source
- Code requirements: safety, licensing, building code requirements, and oil, natural gas/propane or electric code requirements
Average Furnace Operating Costs
After the initial purchase, the cost of running a furnace will vary depending on its type, efficiency, and heat source. Gas and propane will cost the least to run, where electricity and oil will be on the more expensive side. Each type of furnace has various efficiency ratings and the more efficient the furnace, the less it will cost to run over time. Read more about gas, oil, electric, and propane furnaces in the types of furnaces section.
Government Rebates
Various government and utility provider incentives and rebates are available for upgrading the energy efficiency of your home. Ask us about the latest programs and how you may qualify.
Furnace Financing Options
Buying
The majority of providers offer a variety of ways to purchase your furnace. Make sure to ask about your options which may include making a one-time payment, deferred payments or financing programs.
Finance

New Furnace Installation
It is important to note that a furnace works with your home’s whole ventilation and cooling system, and we highly recommend updating your complete HVAC system at the same time to ensure the equipment is compatible.
Once the right furnace type, size and efficiency is decided, your HVAC expert will begin the installation process. Most furnaces can be installed in one day (including removing the previous heating system). However, depending on the amount of existing ductwork, the installation can take up to 3 days.
Types of Furnaces
There are four main types of furnaces: natural gas furnace, propane furnace, electric furnace, and oil furnace. The most popular type of furnace for homes is natural gas. It’s important to find a furnace that matches your budget and desired efficiency level. The following section discusses the four types of furnaces that are common in U.S..
The most popular type of furnace for homes is a natural gas furnace. A gas furnace is the least expensive to operate run and costs $5,000 to $7,000+ to purchase upfront, depending on efficiency. Typically, a gas furnace operates at an AFUE of 95-98% which makes it the second most efficient out of the four.
Gas furnace components include the thermostat, electric controls, gas valve, burners, heat exchanger blower, ducts, and ventilation system.
How It Works
Once the thermostat turns on the furnace, a gas control valve opens and regulates the fuel supply. A pilot flame or ignitor lights the fuel. This flame from the burner fires directly into the primary heat exchanger. The hot exhaust gases move through the internal heat exchanger passages heating the metal and exit through a vent pipe to the outdoors. A blower assembly is then activated and moves air over the hot external surface of the heat exchanger. This hot air is then circulated through the duct system within the home to heat each room.
Advantages of a Natural Gas Furnace
- These are the most frequently installed furnaces since gas is readily available and is the cheapest method to heat your home
- Highly efficient. Lower energy wastage results in lower utility costs each month
- Natural gas is the least expensive fuel source
Disadvantages of a Natural Gas Furnace
- More expensive than other furnaces upfront due to higher efficiency
- As gas is a combustion heat source, there will always be some energy lost and it won’t be 100% efficient
If you are looking for a reliable source of fuel and have the space for a tank, consider a propane furnace. Generally, propane furnaces are the third most efficient opinion of the four types, ranging from an AFUE rating of 80%-94%. A propane furnace costs $5,000-$7,000+ upfront, depending on the size and efficiency.
The most common components of a propane furnace include a propane tank, heat exchanger, blower motor, and a pilotless igniter.
How It Works
A propane furnace operates similarly to a natural gas furnace. Once the thermostat turns the furnace on, a gas control valve opens and a pilot flame ignites the fuel. This flame from the burner fires directly into the primary heat exchanger. The hot exhaust gases move through the internal heat exchanger passages heating the metal and exit through a vent pipe to the outdoors. A blower assembly is then activated and moves air over the hot external surface of the heat exchanger. This hot air is then circulated through the duct system within the home to heat each room.
Advantages of a Propane Furnace
- One of the cleanest burning fuel options
- Highly efficient, making it the second cheapest type of furnace to run
- Typically has a long lifespan
Disadvantages of a Propane Furnace
- Expensive upfront costs
- Need to monitor fuel levels and refill the fuel tank
An electric furnace relies on electricity as the heat source and is a reliable option for homes without natural gas supply. A typical electric furnace operates at an efficiency of 100% because there are no combustion by-products and can cost anywhere from $1,000 to $3,000 upfront. Because the cost of electricity is higher, these types of furnaces are the second most expensive to operate.
The main components of an electric furnace include electric elements, circuit board, and blower assembly.
How It Works
Once the thermostat activates the furnace, electricity is sent to the furnace’s electrical elements. These elements are long wires wound into tight coils mounted inside of the furnace cabinet. Due to the wire material quality of these heating elements, these elements can operate at extremely high temperatures in excess of 2,000oF. These electrical elements are designed similarly to a common hair drier. A blower assembly in the furnace is then turned on and moves air past the hot electrical elements. The air picks up the heat from these hot electrical elements and is then circulated through the duct system within the home to heat each room.
Advantages of a Electric Furnace
- Lowest upfront cost
- Easy installation
- Smallest in size
Disadvantages of a Electric Furnace
- Although they are the most efficient, electricity costs more than natural gas so the operating costs will be much higher.
Oil furnaces are sometimes used for homes in areas where gas services are not available. They are not as common as natural gas furnaces. An oil furnace has an AFUE rating of around 80-90% and typically costs anywhere from $3,000+.
The main components of an oil furnace include an oil burner assembly containing a blower, oil pump, oil nozzle and ignition electrodes, heat exchanger, circuit board, ventilation pipes and blower assembly to circulate air. If you are considering an oil furnace, you must have an oil storage tank and a contract with a company that delivers heating oil.
How It Works
Once the thermostat activates the furnace controls, the oil burner assembly is activated and oil and air are sent to the burner head. The oil is then ignited by the ignition electrodes. This flame from the oil burner fires directly into the primary heat exchanger. The hot exhaust gases move through the internal heat exchanger passages heating the metal and exit through a vent pipe to the outdoors. A blower assembly is then turned on and moves air over the hot external surface of the heat exchanger. This hot air is then circulated through the duct system within the home to heat each room.
Advantages of a Oil Furnace
- Heating quality – higher BTU heating value per cubic foot compared to other fuel types
- Lower upfront cost
Disadvantages of a Oil Furnace
- Less efficient than natural gas furnaces. Oil furnaces can max out with an AFUE of 90%, making them less efficient than some entry-level natural gas furnaces
- Oil costs more than natural gas
- Extensive maintenance due to soot and oil buildup
- Chimneys and oil filters require high maintenance
- Need to monitor fuel levels and refill the fuel tank
- As gas is a combustion heat source, there will always be some energy lost and it won’t be 100% efficient
Heat Pump vs. Furnace
A heat pump is an alternative and increasingly popular method of heating your home. While a furnace generates heat by burning fuel, a heat pump moves heat from one location to another. Heat pumps are typically more efficient and environmentally friendly than a furnace, but they may not work as well in very cold temperatures.
These are some of the main pros and cons to consider when deciding between a heat pump and a furnace for your home.
Heat Pump
- Provides heating & cooling
- More energy efficient and better for the environment (runs on electricity and transfers heat, doesn’t generate it)
- More upfront costs
- In colder climates, need to pair a heat pump with a furnace for hybrid heating
- Potential government rebates
Furnace
- Only provides heating
- Less energy efficient and produces more carbon emissions (generates heat by burning fuel)
- Less upfront costs
- Better for colder climates
Common Problems with Furnaces
The most common problems with a furnace are typically related to lack of maintenance. Without regular furnace filter and blower maintenance, the heat exchangers and blower motors will have a shortened life expectancy. Flame sensors also require periodic cleaning and certain types of igniters can burn out due to normal use. In any case, a trained and qualified HVAC technician will be able to diagnose and fix the problem as quickly as possible.
Other problems people experience with their furnaces include:
Check for closed or blocked air vents
If air vents are closed in the home, the temperature in the furnace can build up to be higher than normal and cause the furnace to shut off to protect itself.
Age of your Furnace
The average furnace lasts about 15 years. If you are experiencing poor performance or hear unusual noises, it’s likely time for a replacement.
What's a Thermocouple or Thermopile?
Older furnaces have thermocouples or thermopiles. This is a safety device that helps detect whether your pilot light is on or not. It ensures that the gas valve is not sending gas into a furnace without a working pilot light. Because these devices are in direct contact with the pilot flame continuously, they can burn out and cause the furnace not to provide heat.
Furnace Tips: Troubleshooting & Maintenance
A faulty furnace in the middle of winter can make your home uncomfortable and also be expensive to repair. Before you call a service technician about your unit, there are a few basic diagnostic steps you can perform.
It is important to note that attempting to fix a furnace is extremely dangerous and needs to be done by a trained and licensed professional. We strongly advise you to consult a licensed HVAC technician for any maintenance and repair work.
The Furnace Won’t Turn On
In cases where the furnace will not turn on, be sure to:
- Check that your thermostat is on and functioning.
- Check to make sure the pilot light is on. To relight it, please consult an expert.
- Check your furnace switch.
- Check your circuit breaker at the electrical panel.
- Check your furnace filter and change them if necessary.
- If you own a natural gas furnace, make sure you have paid your gas bill.
You Notice Strange Sounds or Smells
If you hear loud bangs or smell gas, do not operate electrical components. Leave the home immediately and call your gas company. They’ll send an expert to evaluate the risk of a gas leak. Afterward, you can get in touch with an HVAC expert for furnace repairs or replacement.
The Furnace is Noisy
A homeowner most commonly notices the amount of noise their furnace makes after they first move into a new home. This is often because they’re comparing it to their old furnace. One possible reason for the difference is the type of fan motor the furnace has. A single-stage fan only blows at a high setting and will be noisier than a multi-stage or variable-stage fan. The furnace may also be improperly sized for the home causing it to run all the time. Or your furnace may be working harder because of a clogged furnace filter. Start with changing your furnace filter and if the noise persists, call an expert to assess the furnace.
There’s Not Enough Heat
Check your furnace filter if there’s not enough heat in your house. Also make sure the return vents are not obstructed, that furniture isn’t blocking any air vents and that the dampers are open. Make sure the thermostat is reading correctly by comparing it to another device at the point of your thermostat. If these steps were taken and you’re still having a problem, an HVAC professional will be able to help figure out the cause.
The Furnace Keeps Shutting Off
A frequent cause of the furnace shutting off is a dirty filter. After replacing the furnace filter, if the problem continues, then call a professional. This is a strong indicator that there’s a failing part in the furnace.
Routine Maintenance
After the furnace installation, a licensed technician should perform quality and cleaning checks on all major components every 1-2 years to ensure that the unit performs up to the manufactures standards. The furnace’s filters need to be changed once a month or less, depending on the unit’s efficiency. AskHVACPro offers a Furnace Protection Plan with Maintenance that includes same-day service on breakdowns, unlimited service calls, parts and labour coverage and 24/7 customer service.
We suggest getting your furnace inspected and maintained in the summer before the weather cools down.
Have any questions?
We hope this furnace buyer’s guide helps your purchase a furnace that will fit your needs. If you have any additional questions about the types of heating solution best fits your needs, please feel free to contact our sales team.
Furnace Install & Repair Technicians
Local furnace repair specialist with AskHVACPros near you
Areas we serve in Wake County:
- Apex, NC
- Cary, NC
- Fuquay Varina, NC
- Holly Springs, NC
- Knightdale, NC
- Morrisville, NC
- New Hill, NC
- Raleigh, NC
- Rolesville, NC
- Wake Forest, NC
- Wendell, NC
- Willow Spring, NC
